What is Mental Health?
Mental health concerns our emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how we think, feel, and act in our daily lives. Understanding our mental health helps us build better relationships, improve our health, and boost productivity.
Focusing on self-care, recognizing issues early, and adopting effective coping strategies can help reduce stigma and encourage people to seek help when needed.
Differentiating Mental Health from Mental Illness
While mental health includes our emotional, psychological, and social well-being, mental disorders, often referred to as mental illness, include specific conditions that affect mood, thinking, and behavior.
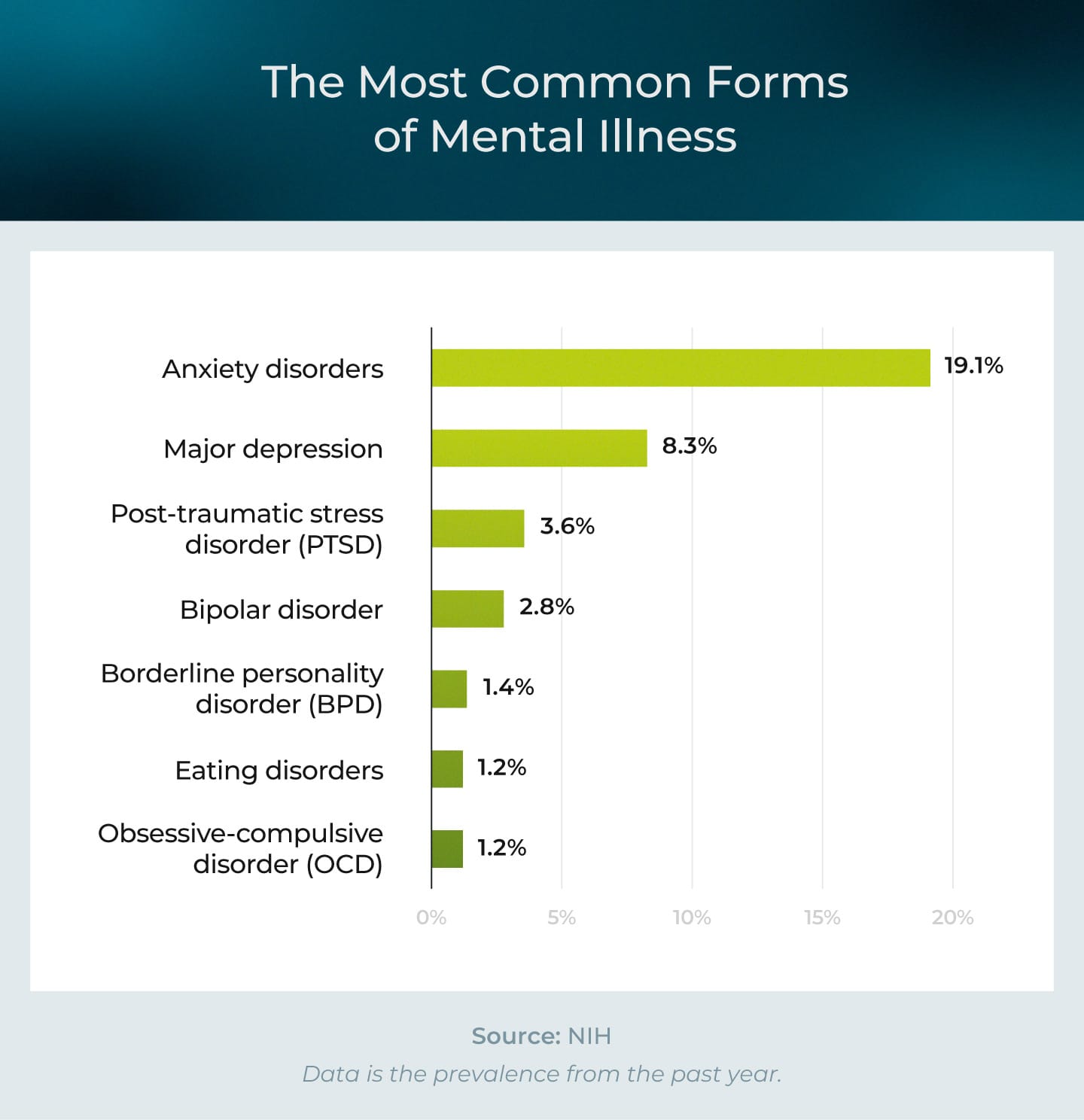
Conditions such as depression, anxiety disorders, panic disorder, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder fall under this category.
Understanding the difference is important: everyone has mental health needs that require nurturing, but not everyone will face their mental conditions in a positive and proactive way.
Like physical health benefits from exercise and a balanced diet, mental health thrives with mindfulness, healthy relationships, and regular self-care.
By recognizing and addressing mental health problems early, we can prevent them from developing into more severe conditions. With a holistic approach, we can guide you through the complexities of mental well-being and help you fit together the puzzle pieces to a healthier life.
Benefits of Good Mental Health in Real Life
Good mental health is essential for a fulfilling life. It strengthens emotional balance, resilience, relationships, and cognitive skills. It helps us communicate and think creatively and enriches our lives.
Addressing our mental health needs is fundamental to ensuring our overall well-being and ability to function at the highest possible level.
Improved Relationships Enhance Quality of Life.
Good mental health is essential for building and maintaining healthy and meaningful relationships. With a solid mental foundation, we can communicate clearly and intentionally, show empathy, and manage conflicts positively.
Improving our mental well-being helps us make deeper and more meaningful connections, understand others, and build mutual trust and respect.
As we strengthen our emotional depth, we strengthen our personal ties with family and friends. We also experience a boost in our professional capacity to collaborate more effectively with co-workers and clients. By nurturing mental wellness, we create a more supportive personal and professional environment for relationships to flourish, fostering a greater sense of community and belonging.
Greater Coping Abilities
Strong mental health allows individuals to utilize effective coping mechanisms, such as problem-solving skills, emotional expression, and seeking and asking for support. These mechanisms make navigating challenging situations at work and home more manageable.
Building resilience allows us to build emotional intelligence, bounce back from escalating stress and disappointing setbacks, and maintain balance in confusing and troubling times. By prioritizing our mental wellness, we equip ourselves with the tools necessary to manage anxiety, depression, and other overwhelming emotions.
This holistic approach helps with immediate stressors and lays the foundation for enduring emotional and psychological stability.
Factors Affecting Mental Health
Mental Health Professionals understand the many causes of mental illness by examining three major areas: Biological, Psychological, and Social Factors.
Biological Factors
Biological factors are critical to our mental health, and when life’s challenges disrupt our well-being, understanding these elements can help you reconnect and restore balance.
Genetics, brain chemistry, and physical health are all parts of this intricate balance.
For instance, genetic predispositions can make individuals more susceptible to psychological conditions like clinical depression and schizophrenia, especially if there’s a family history of such conditions.
Neurotransmitter imbalances, such as low serotonin levels linked to depression or dopamine irregularities, influence mood and behavior.
Chronic illnesses, hormonal shifts, and even nutritional gaps can affect mental health. By recognizing these biological aspects, mental health professionals such as psychologists and psychiatrists can develop comprehensive treatments and interventions, offering a holistic approach to enhancing mental well-being.
This integrated perspective helps you navigate the complexities of mental health, bridging gaps between legal and financial trouble with wellness resources.
Psychological Factors
Psychological factors play a crucial role in our mental health. Elements like personality, thought patterns, and emotions continuously interact, shaping how we perceive and respond to the world.
For instance, individuals with a positive outlook and strong self-esteem often manage stress more effectively, maintaining emotional resilience and a robust outlook toward life.
Conversely, obsessive negative thoughts, low self-worth, and unresolved childhood emotional trauma can lead to conditions such as adult depression and self-destructive behavior. It is a scientific fact childhood physical and emotional trauma (including bullying) can linger unresolved and impact our mental well-being well into our later lives.
Addressing these psychological elements can help us develop healthier coping mechanisms and build a more resilient mental framework, empowering us to live more fulfilling and balanced lives.
Trauma and Stress
Impact of Trauma on Mental Health
Trauma can significantly affect mental health, often resulting from early experiences like sexual and physical abuse, accidents, or witnessing violence. The psychological scars from traumatic events can alter one’s mental state, leading to conditions like PTSD, anxiety, and depression.
Traumatic memories may disrupt daily life, triggering intense emotions and hindering normal functioning. Acknowledging these experiences is crucial to healing and helps one regain normalcy and control.
Therapeutic interventions like counseling, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and support groups can manage trauma’s lasting effects. The growing areas of integrative psychology (Jungian Therapy) and transpersonal psychology are helping people make more sense of their lives and purpose.
Stress and Its Effects
Stress is an unavoidable part of life that can impact mental health if not managed well. Escalating stress from job burnout, divorce, or serious financial issues is highly destabilizing and can lead to a worsening of health problems like anxiety, depression, and heart disease. It can diminish coping abilities, creating a cycle of mental strain, anxiety, and depression. These conditions can often lead to dangerous addictions such as drug and alcohol abuse, as well as unhealthy eating disorders.
Managing stress through mindfulness, exercise, and time management can help mitigate its effects. Developing healthy coping strategies can transform stress into a manageable part of life, leading to a more balanced and fulfilling existence.
Social Factors and Relationships
Social factors and relationships hold significant sway over our mental health.
Building positive connections with family, friends, and colleagues can be the key to finding support, companionship, and a sense of belonging. Social networks act as a safety net against stress, providing emotional and practical help when needed.
On the flip side, strained relationships or social isolation can lead to feelings of loneliness, depression, and anxiety. Investing effort in nurturing healthy relationships can increase happiness, emotional security, and improved mental well-being.
By fostering strong social ties, individuals can solve their mental health problems and find greater life satisfaction.
Environmental Influences
Statistic: Impact of Depression on Work: Depression is a leading cause of disability, costing the global economy $1 trillion annually in lost productivity.
Environmental influences play a key role in mental health, spanning various factors like living conditions, work environments, and community resources. A stable, safe, and supportive setting is vital for good mental health.
Conversely, challenges such as pollution, overcrowding, or unsafe neighborhoods can contribute to heightened stress and anxiety.
By connecting you to green spaces, recreational facilities, and community services, we enhance mental well-being through opportunities for relaxation, physical activity, and social interaction.
By understanding and improving these environmental influences, we aim to foster resilient, thriving communities and promote mental health.
How to Improve Mental Health?
Improving mental health is a journey with many parts, and it involves finding strategies that fit your personal needs.
Here are a few ways to boost your mental well-being:
- Get Moving: Activities like walking, cycling, or yoga can lift your mood by releasing feel-good endorphins. Plus, exercise helps you sleep better and feel more confident. Another helpful choice that combines physical with mental wellness is movement therapy.
- Eat Well: Avoid food addictions. Eating a balanced diet full of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins can boost your mood and brainpower. Omega-3s in fish and flaxseed are especially good for mental health.
- Sleep Enough: Good sleep is super important for your mind and emotions. Stick to a sleep schedule and make your bedroom cozy to help improve your mental health.
- Practice Mindfulness: Try mindfulness, meditation, or deep breathing exercises to reduce stress and feel more at peace.
- Stay Connected: To combat loneliness, keep strong ties with family, friends, and your community. Joining group activities or volunteering can strengthen these bonds. Bonding with a pet can be great therapy for our emotional well-being.
- Consider Therapy: Talking to a psychologist, counselor, or psychiatrist can offer useful insights and coping skills. Therapies like positive psychology are great for dealing with mental health challenges.
- Manage Stress: Find healthy ways to handle stress, like managing your time, setting priorities, and taking breaks to avoid burnout. Therapeutic massage, like Reiki, has helped many people with unresolved emotional issues.
- Watch Substance Use: Cutting back on alcohol and avoiding drugs can help keep mood swings and anxiety at bay.
- Enjoy Your Hobbies: Dive into activities you love, whether dance, art, or music. They bring joy and achievement, both essential for feeling good mentally.
- Ask for Help: Know when to reach out. Whether it’s to mental health professionals or support groups, seeking help can make a difference in managing mental health issues.
Integrating these strategies into your life can improve mental health and a more fulfilling, balanced lifestyle.
What Mental Health Care Services Are Available?
Statistic: About 1 in 5 adults in the U.S. experiences mental illness each year, according to the National Alliance on Mental Illness.
Types of Mental Health Professionals
Understanding the diverse types of mental health services of mental health professionals is essential in navigating the care you or a loved one might need.
Each professional plays an important role in addressing mental health issues, offering specialized skills and perspectives to promote mental well-being.
- Psychiatrists: Medical doctors specializing in diagnosing, treating, and preventing mental illnesses. They can prescribe medications, provide therapy, and manage complex psychiatric conditions.
- Psychologists: Professionals with advanced degrees (Ph.D. or Psy.D.) in psychology. They assess and treat mental health conditions through therapies like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and psychotherapy but typically cannot prescribe medications.
- Licensed Clinical Social Workers (LCSWs): Social workers with specialized training in mental health. They provide counseling, connect clients with resources, and advocate for patients’ needs within the community.
- Marriage and Family Therapists (MFTs): Experts in relational dynamics who provide therapy to individuals, couples, and families, addressing issues within interpersonal relationships and family systems.
- Counselors: Professionals with degrees in counseling who offer guidance and therapy for a broad range of issues, such as stress, anxiety, and life transitions. They include Licensed Professional Counselors (LPCs) and Licensed Mental Health Counselors (LMHCs).
- Psychiatric Nurse Practitioners: Advanced practice nurses who can diagnose, treat, and manage mental health disorders. They often provide medication management and therapeutic services.
- School Psychologists: Specialists in the educational system who support students’ mental health, learning, and behavioral issues through assessments and interventions.
- Occupational Therapists (OTs): Experts who assist individuals in improving their ability to perform daily activities. In mental health settings, they focus on developing coping skills and life skills for better functionality.
Therapists and counselors are trained to help manage many mental health conditions, from anxiety to depression, offering strategies tailored to each individual’s needs.
By understanding the variety of mental health professionals available, you can make informed decisions about seeking the right support tailored to your unique needs.
Goals Of Mental Health Counseling
Mental health counselors are highly trained professionals licensed by the state. Unlike medical doctors, counselors are not licensed to prescribe medication.
Counseling is more a form of talk therapy that focuses on supporting clients to deal with emotional issues that are causing stress, anxiety, and depression.
Statistic: Studies show that approximately 75% of people who engage in therapy experience some benefit.
General goals of the mental health counselor
The overall goal of counseling is to assist clients in their personal and emotional development through talk therapy that focuses on overcoming obstacles that are causing emotional distress.
The counselor may encourage the client to identify issues causing confusion or distress. The main goal is to understand the causes of that behavior and help the client find ways of resolving their problems in a healthy and sustainable way.
Focusing on the client’s issues
Counseling is often used to assist a client in making better and more informed decisions, which supports the goals the client wishes to achieve through the counseling process.
Counseling also helps the client manage their primary relationship. Ultimately, counseling is directed toward helping the client focus on issues that bring the client closer to a genuine sense of purpose and well-being.
Establishing a supportive and safe space
The counselor’s immediate goal is to create a supportive and safe environment for the client.
The counselor seeks ways to better understand the client. In contrast, the client attempts to better understand the counseling process and the counselor.
A client wants to know whether opening up and trusting the counselor is safe. Does the counselor understand what she is doing, and does the counselor genuinely have my best interests front and center?
Examples of Specific Goals of Counseling
- Developing new ways of avoiding reactive and unproductive behavior
- Helping clients improve the quality of their close relationships
- Cultivate a client’s inner and outer potential
- Assisting a client in finding new ways of reducing stress and anxiety
- Finding ways to identify and stop self-destructive behavior
- Encouraging clients to engage in positive thinking
- Assisting clients to acknowledge and stop addictive behavior
- Assisting clients in defining their personal goals
- Assisting clients in developing healthy decision-making skills
Different Types of Counseling Professionals
Counselors handle all kinds of cases. It is not unusual for counselors to treat domestic abuse victims or spouses who need assistance in keeping their marriage together.
Counselors, particularly Marriage and Family therapists (MFT), are uniquely qualified to assist children in emotionally adjusting to parental separation or divorce.
Another area of counseling is anger management, which is often a learned behavior and requires the counselor to assist the client in reducing impulsive or destructive expressions of anger.
Finally, certified drug counselors can assist clients with drug and alcohol abuse and other drug dependency conditions.
Consider connecting with an online counseling service for more information and scheduling a one-on-one appointment to discuss your questions and issues.

Community Resources and Support Groups
Support groups and community resources are crucial for mental health, offering connection and shared experiences for those facing similar challenges, such as mental health disorders or addiction. Engaging in these groups helps individuals find comfort and insights.
Communities offer various mental health services, including local health departments, community centers, nonprofits, and online platforms. Each offers different types of support. Exploring these resources and consulting primary care providers can help individuals access the right mental health services.
Technology and Mental Health

Mental Health Apps
Mental health apps have revolutionized mental health care by providing accessible support anytime and anywhere. These apps offer guided meditation, mood tracking, virtual therapy, and cognitive-behavioral techniques.
They include features like mood journals, stress-relief exercises, and mindfulness activities. While not a replacement for professional treatment, they complement traditional methods, offering immediate relief and promoting self-awareness. Ensure the app is backed by clinical research for effectiveness and safety.
Today, there are numerous mental health apps designed to address different aspects of mental wellness, such as stress management, anxiety reduction, and therapy sessions.
Notable apps include Headspace and Calm for meditation and relaxation, Moodfit for mood tracking, Talkspace and BetterHelp for online therapy, and Sanvello for stress management.
These apps offer various features and subscription options to help users improve their mental health. Choosing an app that meets your needs and ensures data privacy is important.
Common Misconceptions about Mental Health:
Misconception #1: Mental health and mental illness are the same.
Reality: Mental health refers to overall emotional, psychological, and social well-being, whereas mental illness describes specific disorders like anxiety or depression.
Misconception #2: Good mental health means always being happy.
Reality: Good mental health involves managing emotions and coping with life’s challenges, not constant happiness.
Misconception #3: Mental health problems only happen to certain people.
Reality: Anyone can experience mental health issues, regardless of background or life circumstances.
Misconception #4: Therapy is only for severe mental illness.
Reality: Therapy can benefit anyone, helping to address stress, improve relationships, and enhance well-being.
Misconception #5: Self-care is a luxury, not a necessity.
Reality: Self-care is fundamental for maintaining mental health, helps prevent burnout, and improves resilience.
Five Common Fears Related to Mental Health:
Fear #1: I’m scared to show I am a weak person.
Reality: Finding help is a sign of strength. Self-awareness is essential to our mental growth and improved well-being.
Fear #2: I’m concerned that mental health treatment will change who I am.
Reality: Treatment is about helping you manage your challenges, not changing your personality.
Fear #3: Therapy will be too expensive. I simply can’t afford it.
Reality: Many affordable options exist, including community resources and online platforms like Talkspace or BetterHelp.
Fear #4: I’m worried that psychological medication will make me lose control.
Reality: Mental health medication is carefully prescribed and monitored to help restore balance, not control your mind.
Fear #5: I’m concerned that talking about mental health will only make matters worse.
Reality: Addressing mental health concerns early can prevent them from escalating, leading to better outcomes in the long run.
Conclusion
Maintaining good mental health is vital for overall health, fostering a sense of well-being and enabling individuals to thrive in their daily activities.
Effective counseling can help individuals manage emotional challenges, improve relationships, and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
Different types of counseling professionals, from Marriage and Family Therapists to Certified Drug Counselors, are equipped to address a wide range of mental health issues.
If you or someone you know is struggling with a mental health condition, it’s important to seek help from a qualified professional.
The sooner you seek support, the faster you can begin the journey toward healing and recovery. Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness.
Suicide National Hotline:
Sources and References
Habits that destroy our mental health | RBC-Ukraine.
The Role of Spirituality and Mindfulness in Modern Life – ArogyaBhava.
Can Optimism Help Your Anxiety? – Life Coach Hub.
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Treatment in San Rafael, CA.
How Does Behavioral Health Impact Your Well-Being?
The Role of Masculinity in Addiction and Recovery.
Speak Out About Mental Health.