Homelessness
According to the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development’s annual report, as of January 2023, there were approximately 582,462 homeless people in the United States. This number includes people sleeping outside, in emergency shelters, or in transitional housing.
People experiencing homelessness face a myriad of challenges that go beyond the lack of stable housing. These disruptive life-changing challenges are often interrelated and cumulative, making it difficult to overcome homelessness.
According to the National Alliance to End Homelessness and the Urban Institute, many factors contribute to homelessness, including those facing:
- Life-Changing Emotional Instability
- Life-Changing Legal Challenges
- Life-Changing Economic Challenges
- Life-Changing Physical Health Crisis
- Addiction and Substance Abuse
- Extreme Poverty Without Family Support
- Domestic Violence
- Shortage of Types of Shelters
- Lack of Support Services
- Premature Discharge from Institutions
- Lack of Public Social Safety Nets
The Challenges of Being Homeless
Being homeless in America is often a personally damaging and emotionally traumatic experience. People who are homeless face many challenges, including finding safe places to sleep, getting enough food, staying warm, maintaining cleanliness, securing belongings, accessing healthcare, and managing mental health issues related to alcohol and drug addiction.
These challenges, compounded by discrimination and stigma, make recovery and reintegration into society extremely difficult.
What Are the Risks of Homelessness?
Finding a safe place to sleep
Many homeless people are forced to sleep on public streets, parks, or other areas, which can be physically and emotionally dangerous.
Getting enough to eat
Many homeless people do not have enough money to buy food and often rely on food banks or soup kitchens to get enough to eat.
Keeping warm
In the winter, homeless people can be at risk of hypothermia. They may have to find ways to stay warm, such as huddling together in groups or sleeping in shelters.
Staying clean
It can be difficult for homeless people to keep clean. They may not have access to showers or bathrooms and must go to great lengths to find clean clothes.
Keeping belongings safe
Homeless people are often forced to carry all their belongings with them. They must be constantly on guard to prevent their belongings from getting stolen or lost.
Accessing healthcare
Homeless people often have difficulty accessing healthcare. They may not have health insurance, and they may not be able to afford to pay for medical care.
Mental health – alcohol and drug addiction
Many homeless people have mental and emotional health challenges which have led them to alcohol and drug abuse. Any combination of these issues can make it extremely difficult for them to recover and get back on their feet.
In addition to these challenges, homeless people often face discrimination and stigma. They are often treated poorly by the general public. They are denied employment opportunities that most other people take for granted.
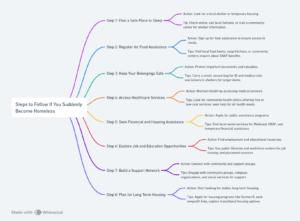
Steps to Follow If You Suddenly Become Homeless
Facing homelessness can be overwhelming, but knowing what to do next can help you navigate this challenging situation.
Here’s a straightforward guide to help you regain stability:
Step 1: Find a Safe Place to Sleep
- Action: Look for a local shelter or temporary housing.
- Tip: Check online, call local hotlines, visit a community center to find information on nearby shelters or call a local hotline for immediate assistance.
Step 2: Register for Food Assistance
- Action: Sign up for food assistance to ensure you have access to meals.
- Tips: Visit local food banks, soup kitchens, or community centers that offer free meals. You can also inquire about SNAP benefits at social service offices.
Step 3: Keep Your Belongings Safe
- Action: Protect important documents and valuables.
- Tips: Carry a small, secure bag for critical items like your ID and medical information. Use lockers in shelters for larger items.
Step 4: Access Healthcare Services
- Action: Maintain your health by accessing medical services.
- Tips: Look for community health clinics that offer free or low-cost medical services. Don’t hesitate to seek help for both physical and mental health needs.
Step 5: Seek Financial and Housing Assistance
- Action: Apply for public assistance programs.
- Tips: Visit a local social services office to learn about and apply for programs like Medicaid, SNAP (food stamps), and temporary financial assistance.
Step 6: Explore Job and Education Opportunities
- Action: Find employment and educational resources.
- Tips: Public libraries and workforce centers can offer access to job training and placement services, helping you get back on your feet.
Step 7: Build a Support Network
- Action: Connect with community and support groups.
- Tips: Engage with community groups, religious organizations, and social services that can offer guidance, counseling, and companionship during tough times.
Step 8: Plan for Long-Term Housing
- Action: Start looking for stable, long-term housing.
- Tips: Apply for housing programs such as Section 8, seek assistance from housing nonprofits, or explore transitional housing options that can offer a pathway to permanent residency.
How To Access Homeless Services and Resources:
(Above Image) A diagram illustrating options on how to access different types of homeless services.
Homeless Resources in Your State:
| AL | HI | MA | NM | SD |
State Pages Contain Local Maps Rich With Related Resources
Each of the above state pages contains a local map that includes important local resources near you, which you can access now, including links to:
Local Addiction Treatment Centers
Local Community Health Care Centers
Local Homeless Centers
Local Food Banks And Pantries
Local Legal Aid Services
Local Low-Income Housing
Local Mental Health Clinics
Soup-Kitchens
National Crisis Hotlines
Each State Page Provides National Crisis Hotlines Providing Emergency Information you can access now:
Suicide Prevention
Domestic Violence
Elder Abuse
Addiction
ADHD
Alzheimer’s and Dementia
Autism
Caregiving
Eating Disorders
LGBTQ+
Parenting
Self-Harm
Team Trouble
Veterans Crisis
Around 40% of homeless adults have been without a home for more than a year (Source: U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development).
Homeless Resources From Different Sources
Public, Charitable, and Private Services Programs
The homeless resources you will find come from a variety of sources, including charitable and non-profit organizations, federal and state assistance programs, foundations, and local community and private organizations dedicated to the needs of others.
While many no-cost public programs and charitable organizations are available to help, such as shelters, food banks, medical and mental health, and addiction counseling, the growing demand for these services far exceeds the current supply.
Read our articles to learn more about the following public, private, and non-profit resources:
Trouble-Shooter Social Impact Program
In response to these growing needs, we feature local, regional, and national organizations that have positively and substantially impacted the fight against homelessness while demonstrating innovative ideas and practices.
We call these compassionate and successful organizations Trouble-Shooters, and after screening them will feature their organizations and include them in our donation section in their state.
Contact Our Trouble Shooter Program
To apply directly, or if you know or have heard of such an organization, we invite you to contact us directly and share their information by emailing us at: trouble-shooters@prodima.xyz.

FAQ’s
1. What makes it difficult for homeless people to find a safe place to sleep?
Homeless individuals often end up sleeping in public spaces like streets and parks because finding a secure and safe spot is tough. These areas are not only uncomfortable but also expose them to potential dangers, both physically and emotionally.
2. How do homeless people manage their food needs?
With limited funds, many rely on food banks or soup kitchens. These places provide essential meals that help them get through each day without knowing when their next meal will come.
3. What challenges do homeless people face in staying warm during winter?
The cold season is especially tough. Many homeless people risk hypothermia and must find ways to stay warm, which might include using blankets, finding sheltered spots, or huddling with others for warmth.
4. How do homeless individuals maintain cleanliness?
This is a big challenge. Without regular access to bathrooms or showers, maintaining personal hygiene requires creativity and resilience. They may seek out public restrooms or use facilities provided by charitable organizations.
5. What are the risks associated with keeping belongings safe while being homeless?
Since homeless people carry their possessions everywhere, there’s a constant risk of theft or loss. Keeping their belongings safe is a daily challenge and adds to the stress of homelessness.
6. How do homeless people access healthcare?
This is very difficult without health insurance or money. Free clinics and charitable health services are vital for them to receive medical attention when needed.
7. Can you describe the mental health challenges homeless people face?
Many suffer from severe stress, depression, and often substance abuse. These issues complicate their ability to stabilize their lives and find permanent housing.
8. Why do homeless people face discrimination and what impact does it have?
Due to stigma, homeless individuals often face rejection and discrimination, making it harder to find jobs or get help. This treatment worsens their isolation and hampers recovery efforts.
Key Takeaways
- Safe Sleeping Areas: Finding a secure place to sleep is a primary challenge for the homeless, impacting their safety and wellbeing.
- Food Accessibility: Many homeless individuals depend heavily on community resources like food banks and soup kitchens for their daily meals.
- Warmth in Winter: Maintaining warmth during colder months is critical, with many at risk of hypothermia without proper shelter.
- Personal Hygiene: Limited access to hygiene facilities makes cleanliness a continual struggle, affecting health and dignity.
- Healthcare Access: Overcoming barriers to healthcare, especially for those without insurance, is crucial for addressing both physical and mental health needs.